Diabetes, an increasingly common chronic disease, is like a hidden bomb. And diabetes complications are a series of “explosions” that this bomb may trigger. They quietly erode the health of patients and cast a shadow on their lives. Do you know that the harm of diabetes complications is far beyond our imagination? In the following content, we will delve into all aspects of diabetes complications, help you recognize these “invisible killers”, and provide you with effective strategies for prevention and response.
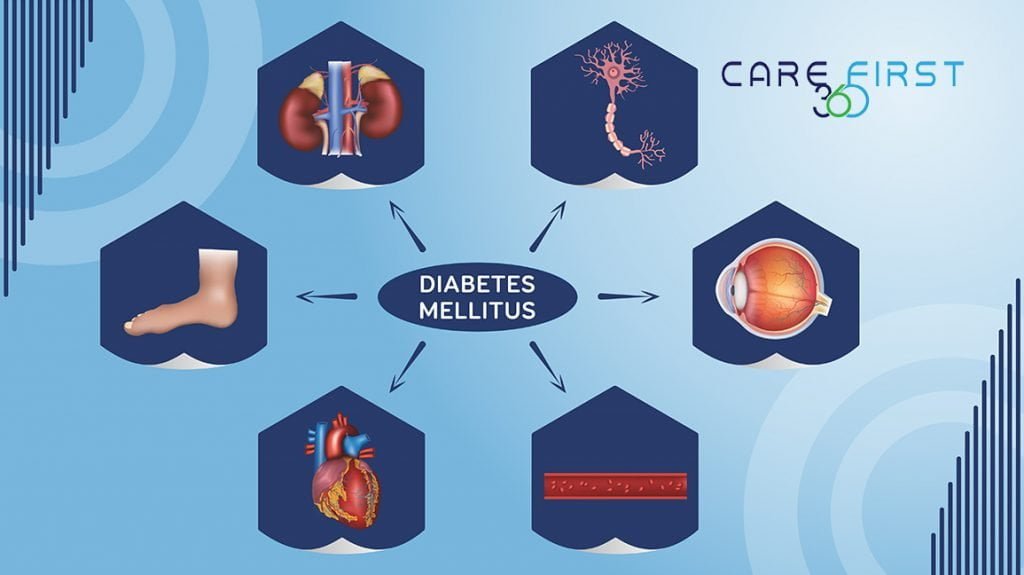
Common types of diabetes complications
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is a serious complication caused by diabetes. The early symptoms are mostly proteinuria. As the disease progresses, edema and hypertension will occur, and eventually renal failure may occur. According to statistics, diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of death in patients with type 1 diabetes and the second leading cause of death in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Retinopathy
Retinopathy can cause visual impairment, which may manifest as night blindness and reduced vision in the early stages, and distortion of vision and loss of visual field in the later stages. Different types of retinopathy have different symptoms, and severe cases can cause blindness.
Neuropathy
It is divided into peripheral neuropathy and central neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy will make patients insensitive to temperature and pain, and easily cause diabetic foot; central neuropathy may cause neurological disorders, diplopia, dizziness, facial paralysis, unstable gait, etc.
Cardiovascular disease
Patients often experience insufficient blood supply to the myocardium, causing symptoms such as chest pain and tightness. It may also lead to heart failure and malignant arrhythmias, increasing the risk of sudden death.
Diabetic foot
Due to damage to nerves and blood vessels, the feet are prone to infection and ulcers, and in severe cases, amputation may be required.
Ketoacidosis
It manifests as worsening symptoms of diabetes, such as extreme thirst, polydipsia, polyuria and weight loss, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and even coma.
Cause
Poor blood sugar control
Long-term poor blood sugar control is one of the main factors leading to diabetic complications. When blood sugar fluctuates or remains at a high level, it can damage organs and tissues such as the kidneys, eyes, heart, and nerves. For example, high blood sugar can cause microvascular disease in the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy; it can damage retinal blood vessels, causing retinopathy.
Metabolic disorders
Diabetic patients often have disorders in sugar, fat and protein metabolism. Unbalanced sugar metabolism reduces the sensitivity of insulin receptors and causes abnormal insulin secretion. Disorders in fat metabolism can lead to elevated blood lipids and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Disorders in protein metabolism can damage kidney function and cause complications such as diabetic nephropathy.
Cardiovascular problems
Diabetic patients are prone to cardiovascular problems, such as abnormal platelet activation and arteriosclerosis. This can lead to insufficient blood supply to the myocardium and cause cardiovascular disease. The research of scholars from Fudan University revealed the phenomenon of high expression and abnormal activation of platelet P2Y12 receptors in diabetic patients, providing new clues to the reasons for the high incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications in diabetes.
Nerve damage
Diabetes can cause nerve damage, leading to nerve conduction and dysfunction. For example, peripheral neuropathy makes patients insensitive to temperature and pain, prone to injury and infection, and develops into diabetic foot; central neuropathy may affect the normal function of the brain and cause a series of neurological symptoms.
Serious harm
Kidney failure
If diabetic nephropathy is not effectively controlled, it may eventually develop into kidney failure. As an important excretory organ of the human body, once the kidney fails, metabolic waste and excess water in the body cannot be discharged normally, which will cause toxins to accumulate in the body and cause a series of serious health problems, such as edema, anemia, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, etc., which greatly reduce the patient’s quality of life and even endanger his life.
blindness
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the main causes of blindness. When the retina is damaged, vision will gradually decline, from blurred vision to complete blindness. This not only makes patients lose the ability to observe the world, but also seriously affects their daily life and work, increases psychological burden, and brings heavy pressure to individuals and families.
Risk of amputation
If diabetic foot is serious, the infection and ulcers on the foot are difficult to heal, and gangrene will form. In order to prevent the spread of infection and save lives, amputation surgery has to be performed. Amputation will limit the patient’s mobility and reduce their ability to take care of themselves, which will have a great negative impact on their psychological and social life.
Cardiovascular hazards
Cardiovascular disease is one of the common complications of diabetes, which increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. Damage to the cardiovascular system can lead to serious consequences such as myocardial infarction and heart failure, seriously threatening the patient’s life safety.
In short, complications of diabetes can cause serious damage to various organs of the body, causing great pain and inconvenience to patients. Therefore, it is very important to prevent and control complications of diabetes. Patients need to actively control blood sugar, have regular physical examinations, and follow the doctor’s advice for treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Ways to prevent complications of diabetes
Strictly control blood sugar
Maintaining stable blood sugar is the key to preventing complications of diabetes. Patients should follow the doctor’s advice and take hypoglycemic drugs or inject insulin on time. At the same time, they should closely monitor blood sugar changes, including fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood sugar and glycosylated hemoglobin, so as to adjust the treatment plan in time.
Healthy eating
A proper diet is essential to prevent complications. Increase the intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat proteins, and reduce the intake of high-sugar, high-fat, and high-salt foods. Control the calories of each meal, avoid overeating, and maintain a balanced and regular diet.
Exercise regularly
Moderate exercise helps control blood sugar levels. You can choose aerobic exercise such as walking, jogging, swimming, yoga, etc., and do it for at least 150 minutes a week. Exercise can also enhance the body’s immunity and improve cardiovascular function.
Regular inspection
Regular comprehensive physical examinations, including eye examinations, kidney function tests, cardiovascular examinations, etc., can help detect signs of complications early and take appropriate treatment measures.
Quit smoking and drinking
Smoking and excessive drinking can aggravate diabetes and increase the risk of complications. Quitting smoking and drinking can reduce the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease.
Keep a positive attitude
A positive and optimistic attitude plays an important role in controlling the disease. Stress and anxiety may cause blood sugar fluctuations, so patients should learn to regulate their emotions and keep a good mood.
Strategies for coping with diabetes complications
Drug treatment
There are corresponding drug treatment plans for different complications of diabetes. For example, patients with diabetic nephropathy may need to take antihypertensive drugs to control blood pressure and reduce kidney damage, and use some drugs to improve renal microcirculation. Patients with retinopathy may need to inject anti-vascular endothelial growth factor drugs to inhibit angiogenesis and protect vision. Patients with neuropathy may use nerve nourishing drugs, such as methylcobalamin.
Surgical intervention
In some severe cases, surgical intervention is necessary. Patients with diabetic foot may need debridement surgery or even amputation if their foot ulcers are severe and gangrene has formed. If diabetic nephropathy develops to the end stage, kidney transplantation or dialysis may be required.
Psychological support
After being diagnosed with complications of diabetes, patients often feel anxious and fearful. At this time, the support of family and friends is crucial, and they should give patients enough care and encouragement. Patients themselves should also actively adjust their mentality, realize that as long as they cooperate with treatment, the condition can be controlled and improved, and strengthen their confidence in defeating the disease.
In short, when facing diabetes complications, patients should maintain a positive attitude, work closely with their doctors, and take effective treatment measures to improve their quality of life and prolong their life.
